In my previous blog, Number Lines―A Lesson in the Planning Stage, I wrote about how I made a detailed five-step lesson plan based on a Tweet I had seen 7 years ago. (Clearly the lesson plan had ample time to marinate.) Here I write about what actually happened when I taught the lesson to fourth graders. Which parts of my five-step plan did I stick to and what changes did I make as I was teaching? What were my reflections afterward? On the written assignment, what did the students show about their understanding?
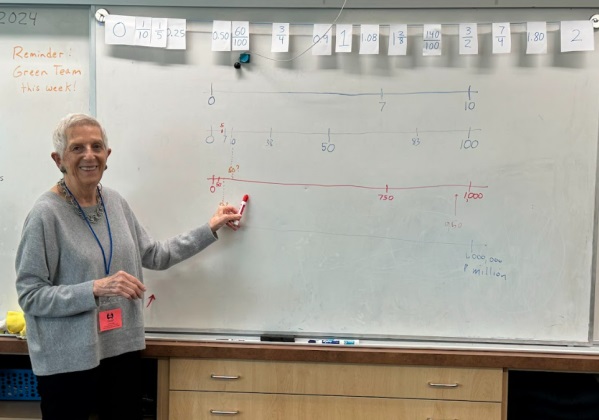

This is the board near the end of the lesson. Read on to learn how we got here.
A Description of the Number Line Routine in the Lesson
In various lessons over the years, I’ve used the routine of moving my finger slowly across a number line, asking students to tell me when to stop when I reach a particular number. I emphasize that we’re estimating, not looking for an exact location. And when the first students call, “Stop!” we chat and decide together if I need to make an adjustment before I mark and label the location .
Before Launching the Lesson Plan
When I began the lesson, I told the class that we were going to estimate where numbers belonged on some different number lines. The class had just completed a unit on fractions and the clothesline at the top of the board had a mix of whole numbers, fractions, and decimals located on it. I told the students that today we were only going to think about locating whole numbers and also that their class number line might help them with the problems I was going to ask them to solve.

Under the clothesline, I drew a number line, marked two points, and labeled them 0 and 10.
What I Had Planned, What I Actually Did, and My Reflections
Now I’ll revisit each of the five steps in my original plan (all in green), then describe what I actually did when teaching the lesson (in blue), and finally offer my reflections about what occurred (in red).
STEP 1
What I Had Planned for Step 1: Start with locating 7 on a number line with 0 and 10 located, introducing the routine of moving my finger across and asking them to tell me when to stop.
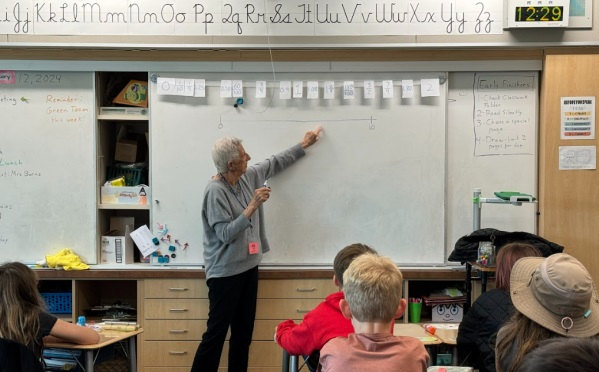
The first step was to locate 7 on a 0–10 number line.
What I Actually Did for Step 1: This is exactly what I did. I told them I’d move my finger across the line and they should say “Stop” when they thought I reached a point where 7 should go. The routine of sliding my finger along the number line was new to the class and it worked, as it typically does, to engage the students’ interest and participation. To locate 7, they said, “Stop!” almost in unison and all agreed that it was close enough. After I made a mark and labeled it 7, I told them I was curious about how they decided where 7 should go. About half a dozen students shared ideas:
“I thought of where 5 went and I went a little further.”
“I decided where halfway was and knew we had to go more.”
“I imagined all the numbers and counted 1, 2, 3, until you got to where 7 would go.”
“I thought of 7/10.”
“I thought of 3/4 and knew that this was a little before that.”
I introduced the vocabulary of “benchmark” and commented that they had used various useful benchmarks―5, one-half, 7/10, and 3/4.
My Reflection for Step 1: Even when a problem seems easy for students, as this was, I think it’s valuable to ask them to explain how they decided. One reason is that this models that I’m interested in not only the answer but also in their thinking. Also, asking them how they reasoned for an easy problem. when the math isn’t a challenge, gives them practice with explaining their ideas.
STEP 2
What I Had Planned for Step 2: Draw another number line underneath that’s the same length, this time with 0 and 100 located, and ask them to locate a few numbers. I’m thinking about 50, 10, 38, and 83.
What I Actually Did for Step 2: As with Step 1, I followed the plan I had made. I drew another line and again marked two points on it, this time labeling the points 0 and 100. Then I used the routine for them to locate the four numbers, stopping after each for students to share their thinking. With each number, more students were interested in sharing. Even when students had similar ideas about where to place a number, they often expressed them in different ways.

Here I’m recording 83, the last of the four numbers I asked them to locate on the 0–100 number line.
My Reflection for Step 2: In my early years of teaching, I did most of the talking in lessons. I’ve worked hard to shift that so students are encouraged to talk. I think when students do the talking it helps them explore ideas, solidify their thinking, and support their learning.
STEP 3
What I Had Planned for Step 3: Next draw another number line, this time with 0 and 1000 located. Have them locate the four numbers I used for the 0–100 number line, but each multiplied by 10―500, 100, 380, and 830.
What I Actually Did for Step 3: With the 0–1000 number line, I changed my plan. It seemed to me that locating 500, 100, 380, and then 830 was too similar to what I had done with the 0–100 number line. Also, I was interested in leaving enough time for them to do an individual assignment. So, for a first experience with the 0–1000 number line, I asked them to locate 750. Before I started moving my finger, I asked them to turn and talk, and I think this helped to result in some interesting explanations. Some compared 750 to where 83 was on the 0–100 number line and stopped a little before, some estimated where 500 would go first, some thought about 750 as halfway between 500 and 1000, one student referenced 3/4.
My Reflection for Step 3: So much was going on here. It seemed that more of the students were showing some intuition about reasoning proportionally, relating the 0–100 and 0–1000 number lines. I didn’t pursue this further, but made a mental note that coming back to this idea more explicitly at another time would be good. But for now, I shifted to Step 4.
STEP 4
What I Had Planned for Step 4: On the same 0–1000 number line, ask them to locate the numbers we used with the 0–100 number line―50, 10, 38, and 83.

Here, after the class had located 750 on the 0–1000 number line, I asked them to say “Stop,” when I reached where 50 would be located.
What I Actually Did for Step 4: I told them that now we were going to locate some other numbers on the same number line. As I had planned, I told them we’d now locate 50. The discussion about where to locate it took longer than I had anticipated. More students wanted to share than before. Some referenced the 0–100 number line. One thought that the number 10 on the 0–100 number line would be helpful, but he wasn’t sure how. Another thought it would be helpful if we knew where 5 was on the 0–100 number line, suggesting that it would go just before the 7. (I located 5 on the 0–100 line as she suggested.) Several thought that the mark on the 0–1000 number line for 50 should go right underneath the 5 on the 0–100 number line. One student said that, from his perspective in the room, it looked as if I should move the mark for 50 a little bit to the right. I asked where 950 might go, thinking it would be another useful reference for locating 50, sort of musing aloud as I drew an arrow to where an appropriate mark for where 950 might be. I don’t think that this was particularly useful. After this discussion, instead of continuing with the other numbers I had intended for them to locate, I moved to the individual assignment.

I decided after the discussion to move on to the individual assignment.
My Reflection for Step 4: The biggest takeaway for me was a reminder that it’s sometimes hard during a class discussion to understand exactly what students are thinking. Their language is often imprecise and their understanding is emerging and sometimes fragile. Sometimes I ask students to explain again, letting them know that I want to be sure I’m understanding their thinking. Sometimes I revoice their ideas and then check with them if I interpreted correctly. Sometimes I ask another student to revoice a classmate’s thinking. There was a range in the students’ thinking, as there typically is during discussions. It felt like the best instructional move would be to give them the individual assignments I had planned.
STEP 5
What I Had Planned for Step 5: Give them an individual assignment with several number lines on which they should locate numbers and an additional option if they’d like to try a challenge.
What I Actually Did for Step 5: I followed this plan. I had prepared a worksheet that had three 0–1000 number lines on it with directions to locate 600, 250, and 60. I included a fourth number line as an optional challenge, this a number line with 0 and 1 million located with the problem to locate 1000.

The students worked independently on the assignment.
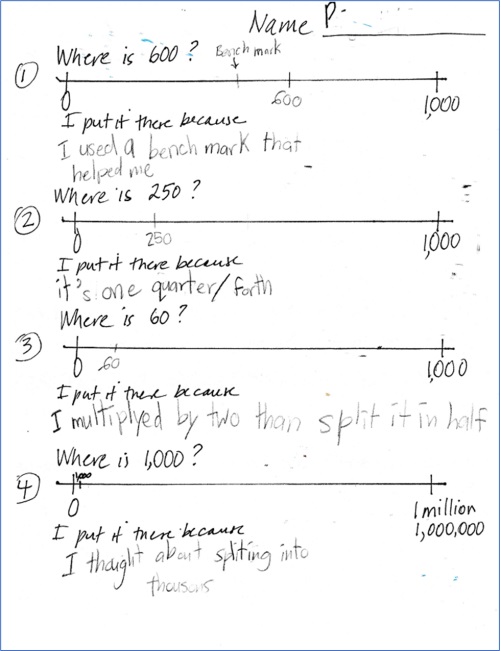
This is the worksheet I had prepared for the individual assignment, completed by one student. Her reasons for the first two were clear, not so with the other two.
My Reflection for Step 5: I think that class discussions are very important for revealing how some students think, both for me and for students to hear their classmates’ ideas. But there isn’t always time to hear from everyone and not all students share in discussions. That’s why individual assignments are so important. Below is the completed work from five morestudents, captioned with my reflections.
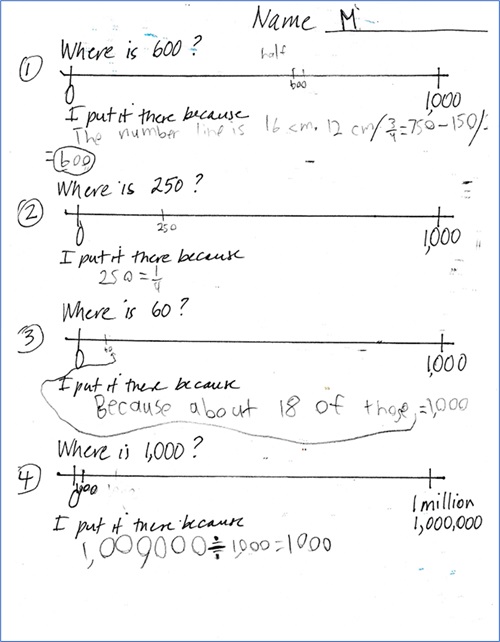
This student relied on fractions to locate numbers on the first two number lines. To place 60, he used an idea that was unique to him in the class, estimating that 60 x 18 was about 1,000 and using that information to locate 60. The last number line shows his understanding of the relationship between 1,000 and 1 million.
Halving 1,000 and then using 500 as a visual benchmark of 500 was this student’s go-to for locating numbers on the first three number lines. Then, for the last number line he started with locating 500,000 and his explanation shows his understanding of the relationship between 1,000 and 1 million.
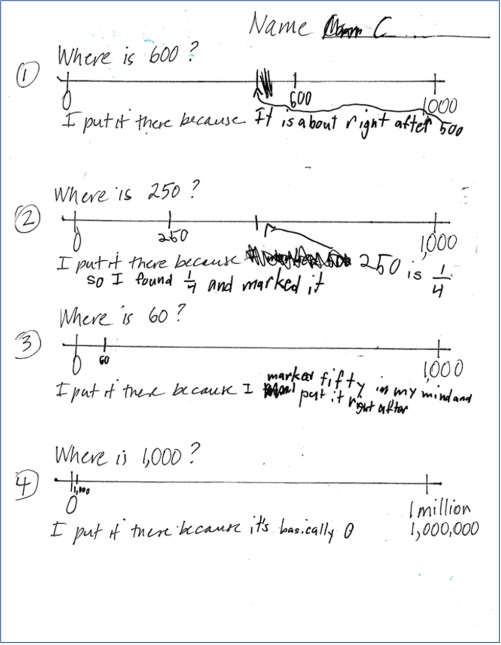
This paper is another example of a student using benchmarks and fractions. Her explanation for placing 1,000 on last number line made me smile.

Using a ruler was helpful for this student for the first two number lines. He told me that he measured in centimeters, and since the line was 16 cm long, it was easy to locate 600 and 250. For the other two number lines, he visually estimated.
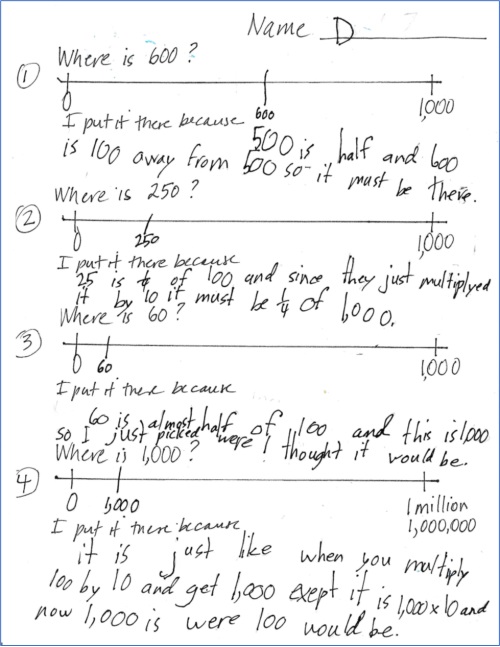
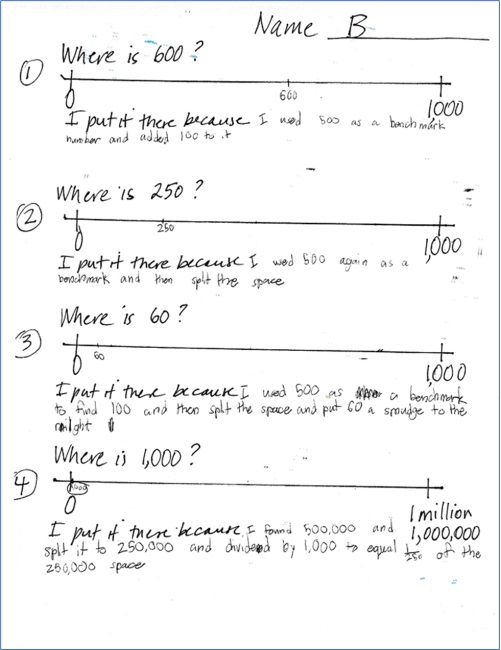
For the first three number lines, this student reasoned using a combination of benchmarks, fractions, and comparing 100 and 1000. His explanation for the last number line shows his emerging understanding of relationships among powers of 10.
Last Thoughts
I loved the lesson, both teaching it and enjoying the students’ engagement. Because I had done so much planning, I felt prepared and relaxed, not distracted by thinking about what I was going to do next. (It’s difficult to teach and think at the same time.) I was able to focus on listening to the students’ thinking.
Finally, many thanks to Amie Levin and her fourth graders at Edna Maguire School in Mill Valley, California. It’s always a pleasure to visit the class.
